Clinical assessment in education utilizes various methods and tools to gather evidence about students' abilities, progress, and needs. By understanding and utilizing these key concepts, educators can make informed decisions to support student learning and development effectively.
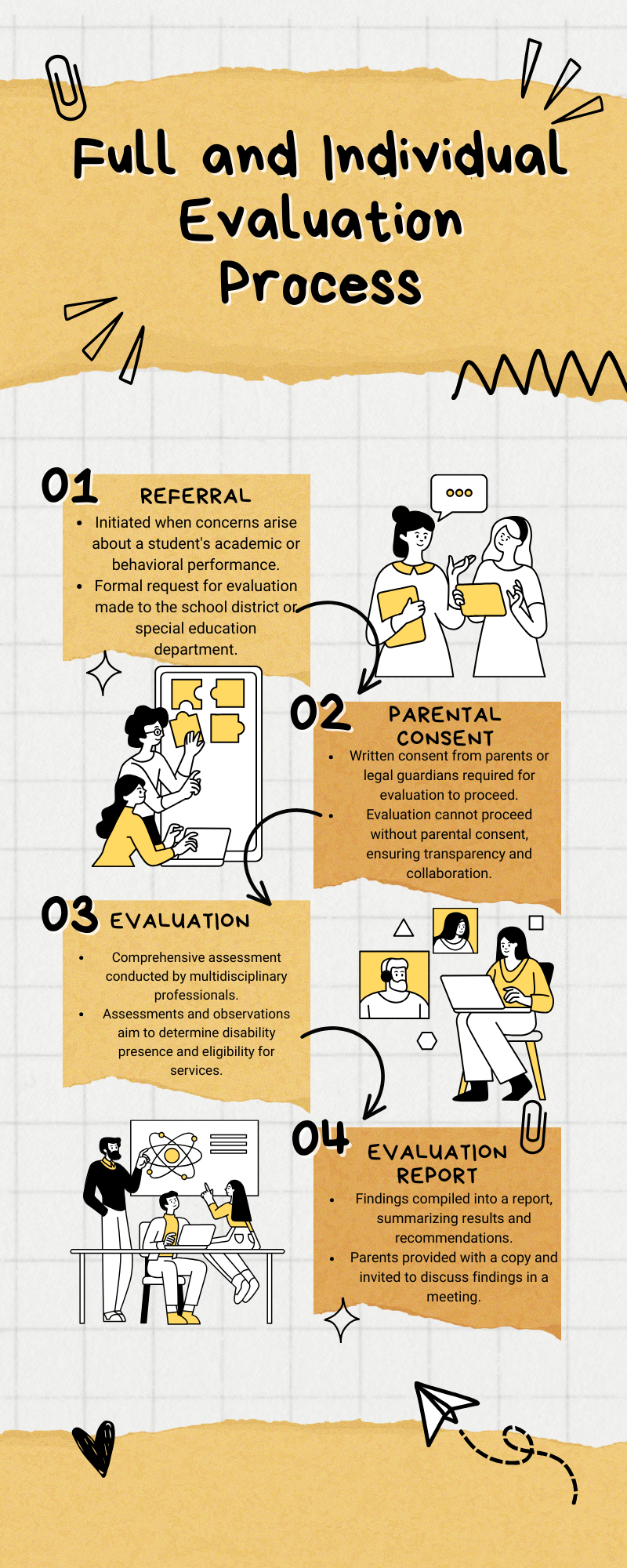
Navigating the Special Education Referral Process: Key Steps and Importance Concepts
The special education referral process is a vital procedure mandated by federal and state laws to identify and evaluate students requiring special education services.
Adaptive Behavior
Adaptive behavior encompasses essential skills individuals acquire to navigate daily life effectively. Let's explore key components and considerations in adaptive behavior assessment and special education eligibility:
Communication
Self-care
Home Living
Social-Interpersonal Skills
Use of Community Resources
Self-Direction
Functional Academic Skills
Work
Leisure
Health
Safety
Intellectual Disability Determination
Score two standard deviations below the mean and a deficiency in two areas of adaptive behavior.
Exclusionary Factors
Factors not primarily contributing to assessment findings:
Access to Quality Education
Excessive Absences
Limited English Proficiency
Vision, Hearing, Motor Impairments
Emotional Behavioral Disorders
Cultural and Environmental/Economic Disadvantages
Emergent Bilinguals and Special Education
Considerations in determining special education eligibility for ELL students:
Ensure need for services isn't solely due to language barrier.
Avoid placement that may stigmatize or disempower students.
Target instruction to second language learning and literacy needs as per legal guidelines.
Understanding adaptive behavior, exclusionary factors, assessment methods, and considerations for English Language Learners is crucial in ensuring accurate special education eligibility determinations and providing effective support to all students. By recognizing these components, educators can promote inclusive practices that empower students to reach their full potential.
Formal Assessments
Monitors knowledge based on:
Norm-Referenced Performance (Class Average)
Criterion-Referenced (Individual Student Performance)
Informal Assessments
Evaluation without standard grading criteria:
Writing Samples
Observations
Project-Based Assignments
Presentations